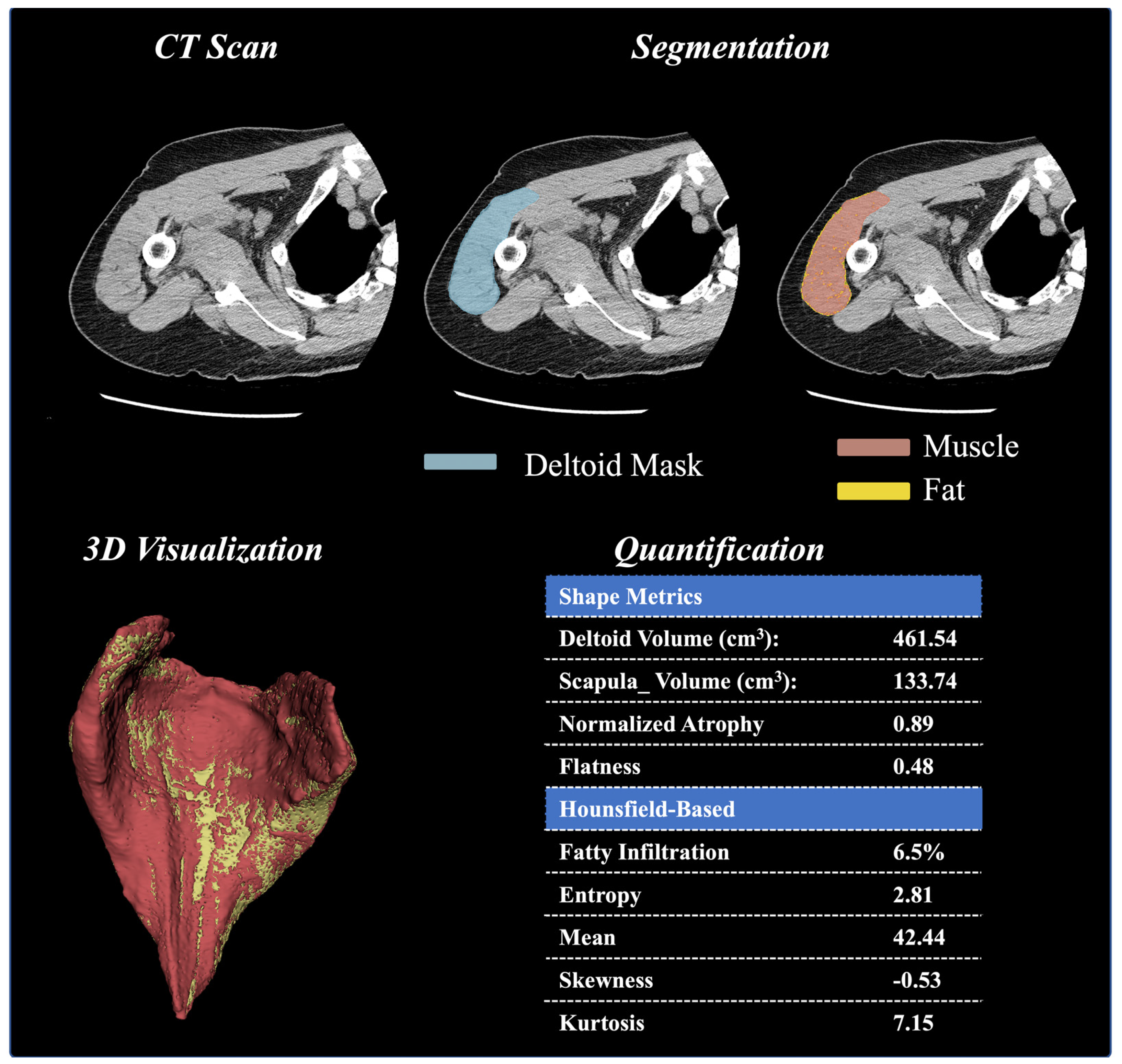
Background: Despite the importance of the deltoid to shoulder biomechanics, very few studies have quantified the three-dimensional shape, size, or quality of the deltoid muscle, and no studies have correlated these measurements to clinical outcomes after anatomic (aTSA) and/or reverse (rTSA) total shoulder arthroplasty in any statistically/scientifically relevant manner. Methods: Preoperative computer tomography (CT) images from 1057 patients (585 female, 469 male; 799 primary rTSA and 258 primary aTSA) of a single platform shoulder arthroplasty prosthesis (Equinoxe; Exactech, Inc., Gainesville, FL) were analyzed in this study. A machine learning (ML) framework was used to segment the deltoid muscle for 1057 patients and quantify 15 different muscle characteristics, including volumetric (size, shape, etc.) and intensity-based Hounsfield (HU) measurements. These deltoid measurements were correlated to postoperative clinical outcomes and utilized as inputs to train/test ML algorithms used to predict postoperative outcomes at multiple postoperative timepoints (1 year, 2–3 years, and 3–5 years) for aTSA and rTSA. Results: Numerous deltoid muscle measurements were demonstrated to significantly vary with age, gender, prosthesis type, and CT image kernel; notably, normalized deltoid volume and deltoid fatty infiltration were demonstrated to be relevant to preoperative and postoperative clinical outcomes after aTSA and rTSA. Incorporating deltoid image data into the ML models improved clinical outcome prediction accuracy relative to ML algorithms without image data, particularly for the prediction of abduction and forward elevation after aTSA and rTSA. Analyzing ML feature importance facilitated rank-ordering of the deltoid image measurements relevant to aTSA and rTSA clinical outcomes. Specifically, we identified that deltoid shape flatness, normalized deltoid volume, deltoid voxel skewness, and deltoid shape sphericity were the most predictive image-based features used to predict clinical outcomes after aTSA and rTSA. Many of these deltoid measurements were found to be more predictive of aTSA and rTSA postoperative outcomes than patient demographic data, comorbidity data, and diagnosis data. Conclusions: While future work is required to further refine the ML models, which include additional shoulder muscles, like the rotator cuff, our results show promise that the developed ML framework can be used to evolve traditional CT-based preoperative planning software into an evidence-based ML clinical decision support tool.
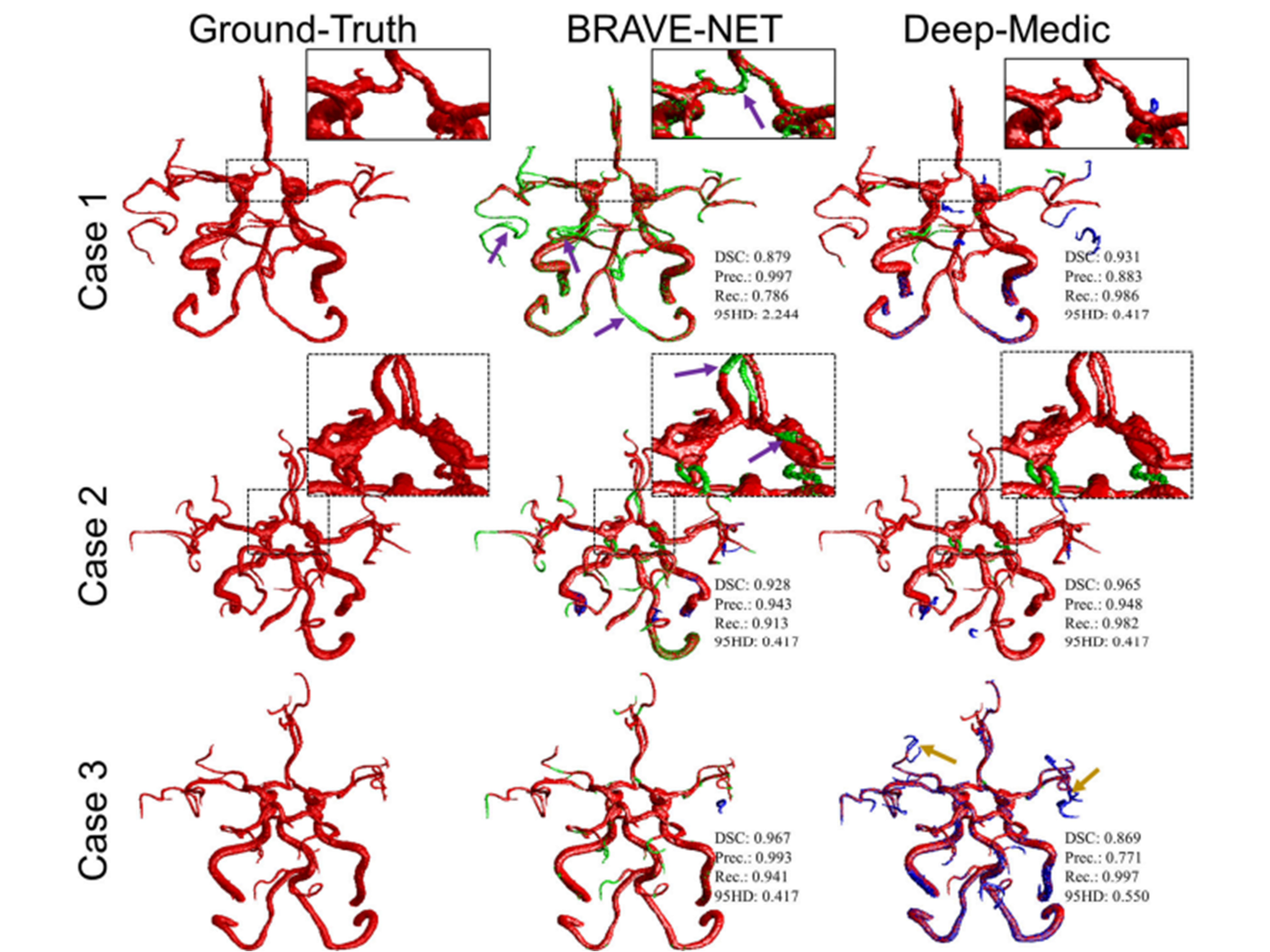
Time-of-flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography is a non-invasive imaging modality for the diagnosis of intracranial atherosclerotic diseases (ICAD). Evaluation of the degree of the stenosis and status of posterior and anterior communicating arteries to supply enough blood flow to the distal arteries is very critical, which requires accurate evaluation of arteries. Recently, deep-learning methods have been firmly established as a robust tool in medical image segmentation, which has been resulted in developing multiple customized algorithms. For instance, BRAVE-NET, a context-based successor of U-Net—has shown promising results in MRA cerebrovascular segmentation. Another widely used context-based 3D CNN—DeepMedic—has been shown to outperform U-Net in cerebrovascular segmentation of 3D digital subtraction angiography. In this study, we aim to train and compare the two state-of-the-art deep-learning networks, BRAVE-NET and DeepMedic, for automated and reliable brain vessel segmentation from TOF-MRA images in ICAD patients. Using specially labeled data—labeled on TOF MRA and corrected on high-resolution black-blood MRI, of 51 patients with ICAD due to severe stenosis, we trained and tested both models. On an independent test dataset of 11 cases, DeepMedic slightly outperformed BRAVE-NET in terms of DSC (0.905±0.012 vs 0.893±0.015, p: 0.539) and 95HD (0.754±0.223 vs 1.768±0.609, p: 0.134), and significantly outperformed BRAVE-NET in terms of Recall (0.940±0.023 vs 0.855±0.030, p: 0.036). Qualitative assessment confirmed the superiority of DeepMedic in capturing the small and distal arteries. While BRAVE-NET consistently reported higher precision, DeepMedic generally overpredicted and could better visualize the smaller and distal arteries. In future studies, ensemble models that can leverage best of both should be developed and tested on larger datasets.Clinical Relevance— This study helps elevate the state-of-the-art for brain vessel segmentation from non-invasive MRA, which could accelerate the translation of vessel status-based biomarkers into the clinical setting.
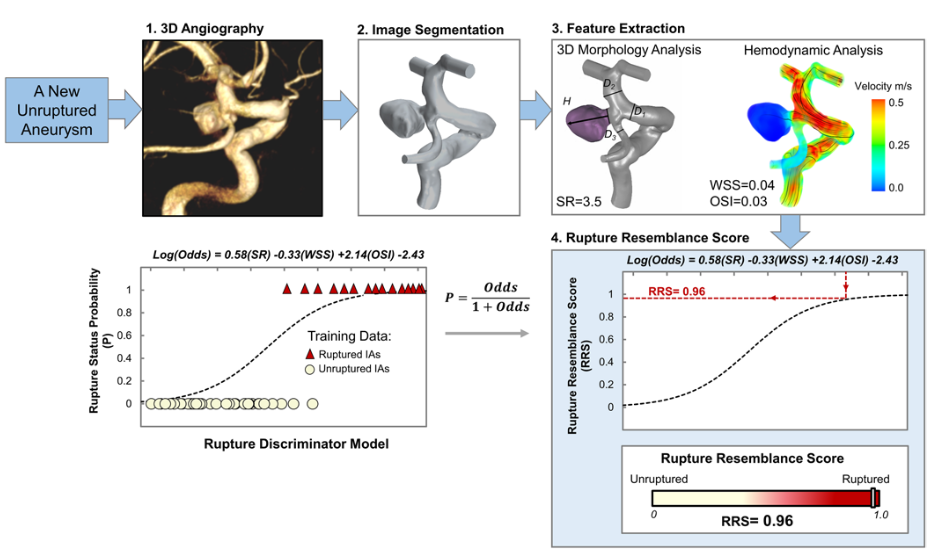
OBJECTIVE Previous studies have found that ruptured intracranial aneurysms (RIAs) have distinct morphological and hemodynamic characteristics, including higher size ratio and oscillatory shear index and lower wall shear stress. Unrup- tured intracranial aneurysms (UIAs) that possess similar characteristics to RIAs may be at a higher risk of rupture than those UIAs that do not. The authors previously developed the Rupture Resemblance Score (RRS), a data-driven com- puter model that can objectively gauge the similarity of UIAs to RIAs in terms of morphology and hemodynamics. The authors aimed to explore the clinical utility of RRS in guiding the management of UIAs, especially for challenging cases such as small UIAs. METHODS Between September 2018 and June 2019, the authors retrospectively collected consecutive challenging cases of incidentally identified UIAs that were discussed during their weekly multidisciplinary neurovascular conference. From patient 3D digital subtraction angiography, they reconstructed the aneurysm geometry and performed computer- assisted 3D morphology analysis and computational fluid dynamics simulation. They calculated RRS for every UIA case and compared it against the treatment decision made at the neurovascular conference as well as the recommendation based on the unruptured intracranial aneurysm treatment score (UIATS). RESULTS Forty-seven patients with 79 UIAs, 90% of which were < 7 mm in size, were included in this study. The mean RRS (range 0.0–1.0) was 0.24 ± 0.31. At the conferences, treatment was endorsed for 45 of the UIAs (57%). These cases had significantly higher RRSs than the 34 cases suggested for observation (0.33 ± 0.34 vs 0.11 ± 0.19, p < 0.001). The UIATS-based recommendations were “observation” for 24 UIAs (30%), “treatment” for 21 UIAs (27%), and “not de- finitive” for 34 UIAs (43%). These “not definitive” cases were stratified by RRS based on similarity to RIAs. CONCLUSIONS Although not a rupture predictor, RRS is a data-driven model that gauges the similarity of UIAs to RIAs in terms of morphology and hemodynamics. In cases in which the UIATS-based recommendation is not definitive, RRS provides additional stratification to assist the identification of high-risk UIAs. The current study highlights the clinical util- ity of RRS in a real-world setting as an adjunctive tool for the management of UIAs.
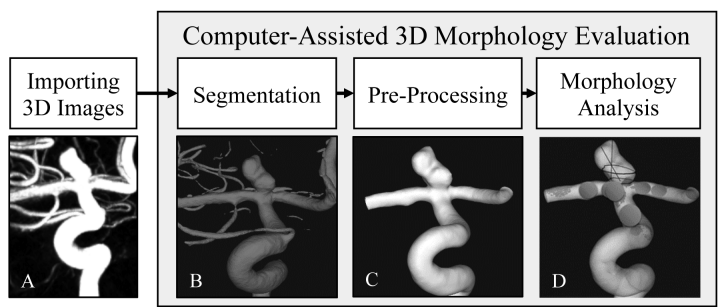
Objective: Precise morphologic evaluation is important for intracranial aneurysm (IA) management. Currently, clinicians manually measure IA size and neck diameter on two-dimensional digital subtraction angiography (2D-DSA) and categorize IA shape as regular/irregular on three-dimensional (3D)-DSA, which might be subject to inconsistency and bias. We investigated whether a computer-assisted 3D analytical approach could improve IA morphology assessment. Methods: Five neurointerventionists evaluated sizes, neck diameters, and shapes of 39 IAs using current and computer-assisted 3D approaches. In the computer-assisted 3D approach, sizes, neck diameters, and undulation index (UI, a shape irregularity metric) were extracted by semi-automated reconstruction of aneurysm geometry using 3D-DSA, followed by IA neck identification and computerized geometry assessment. Results: Sizes and neck diameters measured by the manual 2D approach were smaller than computerassisted 3D measurements by 2.01mm (p<0.001) and 1.85mm (p<0.001), respectively. Applying definitions of small IAs (<7mm) and narrow-necked IAs (<4mm) from the literature, inter-rater variation in manual 2D measurements resulted in inconsistent classifications in the sizes of 14 IAs and the necks of 19 IAs. Visual inspection resulted in inconsistent shape classifications of 23 aneurysms among raters. Greater consistency was achieved by using the computer-assisted 3D approach for size (Intraclass Correlation Coefficient [ICC]:1.00), neck measurements (ICC:0.96), and shape quantification (UI, ICC:0.94). Conclusions: Computer-assisted 3D morphology analysis can improve accuracy and consistency in measurements compared to manual 2D measurements. It can also more reliably quantify shape irregularity using the UI. Future application of computer-assisted analysis tools could help clinicians standardize morphology evaluation, leading to more consistent IA evaluation.